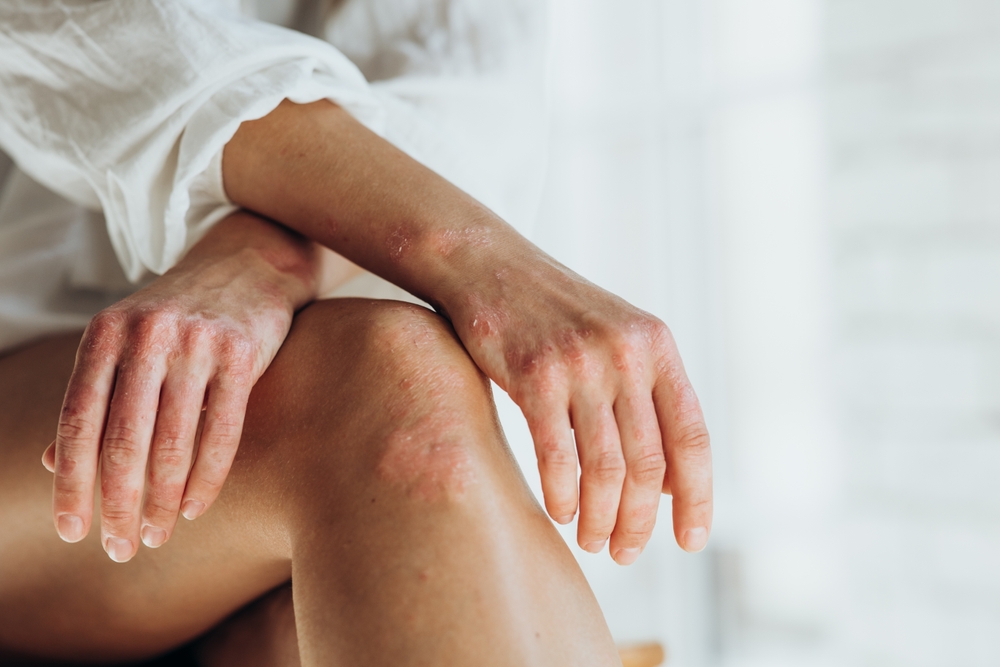
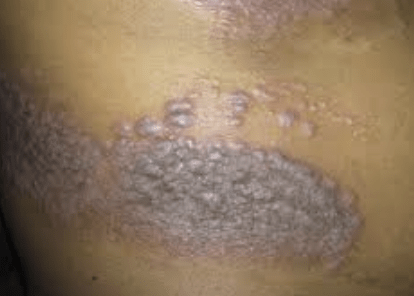
Recent findings from a meta-analysis suggest that probiotic supplementation may reduce Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) and Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI) scores, indicating a potential treatment avenue for psoriasis. Researchers of the analysis, focusing on five studies, assessed the efficacy of probiotic supplements in treating this inflammatory skin condition. The researchers hypothesize that the benefits of probiotics in psoriasis may stem from their immunomodulatory effects on the gut microbiome, such as increasing the enrichment of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells and reducing apoptosis-mediated skin inflammation.
The meta-analysis included randomized controlled trials that investigated the impact of probiotics on psoriasis. The primary outcomes focused on were PASI and DLQI scores, where lower scores indicate milder disease severity. After pooling results from five selected trials with 286 participants, the researchers found that probiotics were superior to placebo in treating psoriasis, as indicated by decreases in PASI and DLQI scores.
Reference: Smith T. Probiotic Supplementation May Serve as Psoriasis Treatment Option, Study Finds. HCPLive. Published April 2, 2024. Accessed April 8, 2024. https://www.hcplive.com/view/probiotic-supplementation-may-serve-as-psoriasis-treatment-option-study-finds